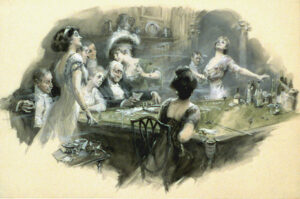The Frontier Gambler is one of the most recognizable stock characters of the American West, usually portrayed as a gentlemanly southerner living outside of the law. Historically, gamblers were of both sexes, came from various professions and class backgrounds, were of many different nationalities, and were part of a well-respected profession. As the west became increasingly populated and domesticated, the public perception of gambling changed negatively, leading nearly all state and territorial legislatures to pass anti-gambling laws to “clean up” their towns. The gambler continues to be a captivating figure in the imagery of the west, representing the openness of its society and invoking its association with risk-taking.
The heyday of gambling in the west lasted from 1850-1910. Gambling was the number one form of entertainment in the west, and nearly everyone living there engaged in it at one time or another. Cowboys, miners, lumberjacks, businessmen, and lawmen all played games of chance for pleasure and profit. Whenever a new settlement or camp started, one of the first buildings or tents erected would be a gambling hall. As the settlement grew, these halls would become larger and more elaborate in proportion. Gaming halls were typically the largest and most ornately decorated buildings in any town and often housed a bar, stage for entertainment, and hotel rooms for guests. These establishments were a driving force behind the local economy, and many towns measured their prosperity by the number of gambling halls and professional gamblers they had. Towns that were friendly to gaming were typically known to sports as “wide-awake” or “wide-open” for their acceptance of gambling.
Most western citizens considered gambling a respectable profession, and those who chose to make a living doing it were respected members of society. “Gambling was not only the principal and best-paying industry of the town at the time, but it was also reckoned among its most respectable,” wrote Bat Masterson in 1907. Professional gamblers ran their games by renting a table at a gambling house and banking it with their own money. Because of this, many professional gamblers settled in one place. To be successful as an established businessman, a gambler needed to cultivate a reputation for fairness and running a straight game. These men were known as “sports” and did not drink, cheat, or swear, paid rent and licensing fees, encouraged customers to run up bar tabs, and did their best to act as historian Hubert Hoover Bancroft put it, “reputable and respectable merchants.” Bancroft distinguishes between three types of professional gamblers, the free-floating professional, the established legit, and the recreational gentleman.
The California Gold Rush of 1849 created one of the largest draws for migrant gamblers, and San Francisco, California, soon became the gambling hotspot of the west. Famous gambling houses included the Parker House, Samuel Dennison’s Exchange, and the El Dorado Gambling Saloon. Portsmouth Square was famous for the many houses that clustered closely around it. Gambling was also popular in the many mining camps throughout California and the southwest. Gambling was so closely associated with the Gold Rush that the overland route to California that passed through Panama became known as the “Gambler’s Route.” Dealers lay in wait everywhere, and it is said that many an expedition to the goldfields ended in camp before it even began. Mining towns outside of California developed large-scale gambling as well. Deadwood, South Dakota; Silver City, New Mexico; and Tombstone, Arizona were all as well known for their many gambling halls and saloons as they were for their rich mineral deposits.

Gambling
Cattle towns in Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Nebraska, became gambling centers. Thanks to the railroad and cattle industries, a great number of people worked in and around these towns and had plenty of money to wager. Abilene, Dodge City, Wichita, Omaha, and Kansas City all had an atmosphere that was convivial to gaming. Not surprisingly, such an atmosphere also invited trouble, and such towns also developed reputations as lawless and dangerous places.
Men were not the only ones who played at games of chance, women placed their bets, and the sight of petticoats at the table was regular. Many women played, dealt, or ran their own houses; this choice of profession offered them the opportunity to attain monetary independence and social stature. One of the most famous was Eleanore Dumont, known more crudely in her later years as “Madame Mustache.” Miss Dumont ran several different houses in Nevada, Idaho, Montana, and South Dakota. Another, Alice Ives, started gambling after the death of her husband. Known more popularly as Poker Alice, she was a readily recognized figure in the west for her nearly 40-year-long career. Kitty LeRoy made use of her sex appeal and flamboyant personality as well as excellent gambling ability to become a force of nature in Deadwood. She had multiple husbands and did not hesitate to get rid of men once she was tired of them. Perhaps they were lucky because Kitty also had a reputation for shooting men.
Frontier gamblers represented many nationalities and races. Especially in California during the gold rush, prospectors came from all over the world in search of gold and naturally played games of chance. This included Mexicans, Chinese, Australians, and Peruvians. Anglo migrants to areas of the southwest with pre-established Mexican populations discovered gambling there waiting for them. Most towns had at least one or two salas or gambling houses. One of the most popular games, monte, originated in Mexico and was adopted and later modified into three-card monte. The Chinese were avid gamblers who brought various games with them to North America, including Fan Tan and several different lottery variants. Chinatown in San Francisco contained many gaming houses and was a popular destination for those seeking to play.
Gamblers preferred fast-paced games allowed them an opportunity to turn a profit quickly. Faro was the most popular game and was known as the king of all games. It was not the only game people played, and monte, Vingt-et-Un (twenty-one), roulette, chuck-a-luck were all popular ways to take a risk. Poker was not initially popular because of its slow pace but gradually increased in popularity as time went on. Not all games required playing cards; dice games such as craps were common, as were games involving a wheeled device, such as roulette or hazard. However, saloons and gaming tables were not the only places to bet, and westerners had a well-deserved reputation of being willing to bet on anything. Horse races became an enormously popular means of wagering, and foot races and boxing matches provided a similar opportunity. Fights between animals were popular, whether cockfighting, dogfights, or even a panther vs. bear battle.
The popular stereotype of the frontier gambler presents a tall, thin male wearing a mustache. He is well-groomed and wears a tailored suit, usually of black. Frequently having a southern background, the frontier gambler is presented as a gentleman in manner and custom and is concerned with maintaining his honor. The gambler possesses a calm demeanor and is cool under pressure, but when crossed, instantly becomes a cold-blooded killer.
The persistent presence of gambling in western mythology shows a strong association with the risk-taking and chance involved both in coming to the west and in everyday life there. In a sense, those who chose to leave their lives and come west were taking a considerable gamble to begin with. Gambling is also strongly associated with extralegal activity and to have that activity practiced so frequently suggests a popular association of the west with a state of lax legal and moral codes.
Several well-known gamblers in the Old West included such names as Bat Masterson, Pat Garrett, Doc Holliday, Lottie Deno, Luke Short, Poker Alice, Soapy Smith, Wild Bill Hickok, Wyatt Earp, Kitty Leroy, Billy the Kid, and Ben Thompson.
Compiled and edited by Kathy Weiser/Legends of America, updated December 2019.
Source: Wikipedia. ![]() Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike
Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike
Also See:
Adventures in the American West